Big O Notation
There are a lot of existing algorithms; some are fast and some are slow. Some use lots of memory. It can be hard to decide which algorithm is the best to solve a particular problem.
"Big O" analysis (pronounced "Big Oh", not "Big Zero") is one way to compare the practicality of algorithms by classifying their time complexity.
Big O is a characterization of algorithms according to their worst-case growth rates
We write Big-O notation like this:
O(formula)
Where formula describes how an algorithm's run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows.
O(1)- constantO(log n)- logarithmicO(n)- linearO(n^2)- squaredO(2^n)- exponentialO(n!)- factorial
The following chart shows the growth rate of several different Big O categories. The size of the input is shown on the x axis and how long the algorithm will take to complete is shown on the y axis.
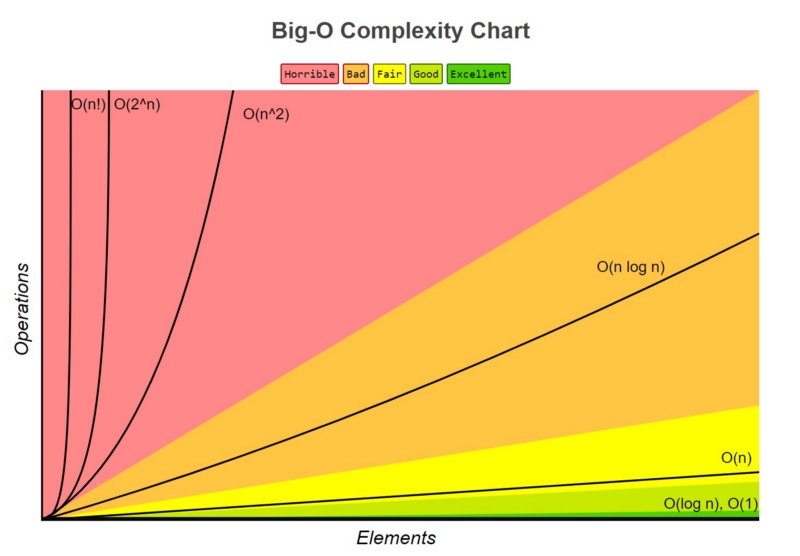
As the size of inputs grows, the algorithms become slower to complete (take longer to run). The rate at which they become slower is defined by their Big O category.
For example, O(n) algorithms slow down more slowly than O(n^2) algorithms.
Click to play video
The Worst Big-O Category?
The algorithms that slow down the fastest in our chart are the factorial and exponential algorithms, or O(n!), and O(2^n).